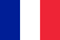
Cystitis is a process of inflammation that affects the inner wall of the bladder.In the early stages, it affects primarily on the mucous membranes, and in severe cases can spread to the organ muscle layer.
According to statistics, nearly 35% of people (especially women) at the age of 20-40 are faced with this pathology, it accounts for up to 67% of all cases of urological disease.
IMPORTANT! Inflammation of the bladder is characteristic of both genders, however, due to anatomical properties, in women it occurs 6-8 times more frequently.The wider, straight and short urethra provides easy access to a variety of urogenital infections.With age, the frequency of incidence in men and women was launched due to the growth of prostatitis cases in elderly men and secondary cystitis.
Diagnostics and pathological treatment are involved in urologists.Women often have to use the help of gynecologists.
Cystitis: the form and type of pathology
Depending on the presence of an internal source of inflammation, 2 types of cystitis are distinguished:
- Main - develop as a free inflammation of the bladder wall;More often found in women;
- Secondary - arises from other diseases of urea or inflammation of the tissue and adjacent organs (for example, with prostatitis in men).
By the nature of the disease, they distinguish:
- acute form;
- Chronic forms - mixed symptoms without pain and burning are characteristic.
In the coverage area, the disease can be:
- amount, or general;
- Focal - for example, the cervical form with damage to the bladder neck;
- With a trigonite ureteral triangle (trigonite).
Note!The focus of inflammation can cover the entire urinary system - in such cases, cystitis is the first clinical manifestation of kidney disease or pyelonephritis.
Given the observed changes in the lesion area, distinguish:
- Catarrhal - a classic acute inflammatory process with damage to only mucous tissue;It is accompanied by severe hyperemia, swelling and the release of serous exudate (serous form);In a neglected case, it can enter into purulent form (with the release of purulent exudate);
- Phlegmonous - a special type of purulent inflammation with purulent damage that spilled into the submucosal layer;
- Granulomatous - accompanied by a large rash on the mucous membranes of the organ;
- Hemorrhagic - the process of inflammation, accompanied by the release of blood in the urine;
- Interstitial - with the involvement of deep muscle layers;
- ulcerative - with the formation of ulcers characteristic of the internal wall mucous membrane;
- In a row - for a short time not a ulcer grown with salt;
- Cystic - with the formation of cysts in the submucosal organs;
- Gangrenous - with the killing of cloth.
Given the reasons, all cases are divided into 2 large groups of contagious and endless cystitis.
Contagious forms They develop under the influence of various urogenital and general infections.Distinguish:
- Specific pathology - pathogens (especially bacteria) - chlamydia, gonococci, and so on;
- The non-specific pathology of the disease is a variety of appropriate pathogenic representatives
Note!In rare cases, cystitis can occur in response to kidney tuberculosis infection.The disease is accompanied by a clear clinical picture.
Non -shiny cystitis - Develops the result of non -biological damage to the mucous membranes of the organ.There are several types of pathological effects:
- Radial - a negative effect on radiation therapy tissue or radio exposure;
- Allergies or autoimmune - the pathological reaction of the body to allergens (especially personal hygiene products) or tissue antigen;
- Traumatic - with minced or cut, with damage to the wall with urine, catheter, foreign body;
- Parasites - under the influence of toxic parasites, especially blood schistosome (flat worm type);Risk zones include mainly tourists in the Middle East and Central Asia;
- Thermal - with burns, when washing with too hot solutions;
- chemical toxic-when exposed to aggressive substances: drugs, concentrated metabolites, toxic substances, and so on;
How Cystitis occurs: the cause of the pathology
Most cystitis has an infectious nature.The causative agent in this case can be a pathogenic-e bacteria.Coli, streptococci, staphylococci, enterococci, and frequent representatives of urogenital-gonococci infection, trichomonas, etc.
However, invasion of microorganisms is not the main cause of the disease.For its successful effects, the body should be weakened by the influence of external and internal factors.These include:
- Chronic infections in other body systems - tooth decay, bowel disease, various forms of acute respiratory virus infection, gynecological inflammation and STD;
- Vitaminosis and hypovitaminosis against the background of an unbalanced diet;
- Physical, nervous, frequent mental hard work, as well as insomnia and lack of night sleep;
- strong psycho stress;
- general weakness of the immune system, including prolonged use of immunosuppressors;
- Hypothermia of the body, the effects of temperature change -are for women sometimes enough to sit on the cold surface to start the inflammation process in the pelvic organs, including the bladder;
- High sexual activity if there is no regular partner (non -traditional sexual practice and unprotected sex are very dangerous);
- Unstable phenomena in the pelvic work of the organs and lifestyle in general, frequent constipation, incomplete emptying due to urethra or bladder tumors, as well as the shallow habits "last to the last";
- Poor or improper body hygiene - in 90% of cases, pathogen cystitis is E. coli, which enters the bladder from the rectum;
- wearing synthetic linen, especially narrow, squeeze pelvic organs;
- the development of abnormal urinary organs;
- injury and surgical intervention on the pelvic organs;
- Acute and fatty foods.
Separately, the cause of the disease should be mentioned by endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus, taking hormone medication) and general fluctuations in the hormone background.The last reason is the characteristics of the female body, when enlargement of cystitis accompanies the period of menstruation, pregnancy or menopause.
Symptoms of disease
The first symptom of cystitis is an increase in urination and discomfort in the lower abdomen.Otherwise, it all depends on the form of the disease and the cause.
General List of possible features:
- frequent urination, sometimes false;
- Urine has muddy colors, blood impurities (hematuria) and pus;
- pain in the lower abdomen (can be given to the lower back);
- engraving and burning in the urinary process;
- persistent sensation of bladder fullness;
- Urine has an unpleasant odor;
- daily or night enuresis;
- Increase body temperature and general weakness.
In rare cases in the form of acute, chills, nausea, vomiting possible.
IMPORTANT! The disease is not characterized by temperatures above 37.5 degrees.In the event of an excess of this indicator, it is necessary to study the entire urinary system - it may be that the inflammation process has reached the kidneys.
In women, pathology is often continued in acute form and is accompanied by a set of classic symptoms.
Men are characterized by chronic diseases with smooth symptoms, often accompanied by signs of disease similar to sexual spheres (for example, balanoposthitis or urethritis).
Diagnostics
The obvious symptoms of the disease allow you to make a major diagnosis after talking to the patient and palpation.The instrumental and additional laboratory examination methods allow for the establishment of the type and form of the disease, identify the pathogen (with infectious lesions) and prescribe the most effective therapeutic complex.
Instrumental diagnostics:
- Echoscopy (ultrasound) - determines the level of inflammation, allowing to assess the state of the urinary and sexual system simultaneously;
- Endoscopy (cystoscopy) - the examination of the bladder using the cystoscope optic system allows you to evaluate the internal integument, identifying the possibility of pathology and neoplasms;performed only after the loss of acute phenomena;
- Cystography is an X -ray exam using contract X -ray.
Laboratory research:
- General urine analysis - check pH levels, leukocyte concentration, red blood cells, proteins and uric acid salts;
- study of urine sediment for more accurate results;
- Baksev - to identify infectious pathogens;
- Tissue biopsy, followed by histological examination;
- PCR-diagnostic diagnostics are possible when identifying sexual infections.
In some cases, doctors may prescribe analysis for blood biochemistry - it allows you to detect body functions with changes in major electrolyte concentrations (potassium, sodium, calcium), and evaluate enzyme system activity.
For women, it is important to conduct gynecological examinations for the presence of "female" inflammation, which is often the cause or consequence of cystitis.
Attention! Often, urea inflammation is a more serious symptom of the disease, therefore, differential diagnosis is required for tuberculosis, prostatitis (in men), cancer tumors, etc.
How is the treatment going?
The acute form of cystitis easily and quickly goes into the chronic, so it is important to respond to the first signs of the disease on time and properly.
Attention! Often, after the first acute manifestation of the symptoms, inflammation freely comes to a bite.This does not mean that the patient has recovered - the disease can go "underground", and a more careful diagnosis of the body is needed to identify the hidden pathological process.
Treatment, as a rule, complex, uses conservative methods.With a competent approach, the results are profitable.Surgical intervention is only needed in the most advanced cases.
List of Appointments:
- drug therapy;
- Unmistakable regime;
- a lot of drinks;
- Compliance with diet.
In chronic form to restore bladder function, physiotherapy complex is given.
Drug:
- Antibiotics - in chronic form, make selection of individual drugs based on bakposev results;
- Diuretics - diuretics increase urine flow, wash pathogen flora and reduce the concentration of irritating substances;
- antispasmodics;
- Vitamin preparations.
To avoid the pathogenic effects of large amounts of chemicals, grades are actively used with cystitis, especially anti -diuretic and diuretic: stubborn, lingonberries, kidney tea (orthosiphon), St.John, spray, chamomile, parsley.Good effects are given by pharmaceutical drugs based on plant ingredients.
Attention! Drink a lot with cystitis necessarily!The minimum amount of pure water is 2 liters.Recommended-2.5-3 liters.
Features -The dietary features:
- excluding all fireplaces, spices -sharp spices, pickles, sugars, smoked and fried foods, as well as alcohol, tea, coffee, sweet soda;Salt from the diet should be removed to the maximum (!);
- reducing the amount of meat, fish, chicken, especially fat types;
- Milk products are consumed in small quantities -low cottages, yogurt, milk, low and non -resolved cheese;
- Increase the use of fresh vegetables and fruits (great priority to watermelon, pumpkin);
- To prevent constipation in the diet, bran content, cereals, and vegetable oils need to be increased.
Characteristics of cystitis in pregnant women
Changing hormone backgrounds during pregnancy creates prerequisites for suppressing the work of the immune system, which increases the risk of developing various inflammatory processes.Small hypothermia, little violation of hygiene regulations as well as normal climate change (the body considers it as stress) can cause bladder inflammation.
When it comes to children, especially in the late stages of pregnancy, the pressure on the bladder due to increased uterus.On the one hand, this creates a stagnant phenomenon in the pelvic area and contributes to the development of cystitis, in turn, exacerbates the manifestation of symptoms, in particular:
- frequency of urine increases;
- The feeling of pressure in the bladder becomes constant and does not stop even after clearing it.
Treatment during pregnancy is difficult because the prohibition of the use of most antibacterial agents-they can affect the full development of the fetus.Alternatively, planting methods are used - the introduction of antibacterial agents of local action directly into the bladder cavity.This procedure is performed at the hospital under the control of medical staff.
Attention! Cystitis during pregnancy is dangerous for complications.High burden on the kidneys during pregnancy requires continuous monitoring of the urinary system and hospitalization immediately in the event of a spread of inflammation to the upper department.
How do I warn this disease?
To prevent inflammation in the urinary system, it is sufficient to comply with the following rules:
- Avoid lower body hypothermia - do not sit on cold surfaces, making sure your feet are warm.
- Exclude sharp and salty products from the diet.
- Treat timely sexual infections, as well as other inflammatory processes (including caries).
- Reject synthetic materials, especially in the composition of the underwear.Avoid narrow pelvic areas and tighten clothes.
- With the presence of inactive work, take a 10-15 minute break with heating.
- Be careful to observe the rules of personal hygiene (especially for women) - when washing and wiping after eradication, all movements should be directed backwards.Lower underwear should be changed daily.During menstruation, it is necessary to change the gaskets and tampons as often as possible.
- Try to urinate on time - at the first "natural call", don't tolerate - this causes urine stagnation and present the bladder wall.Natural norms 5-6 times during the day.
With frequent recurrent cystitis for preventive purposes, you should drink a glass of cranberry juice daily - a clear antibacterial properties will prevent the disease or reduce the frequency of its manifestation.